EIGRP Evaluation Sim
You have been asked to evaluate how EIGRP is functioning in a network.
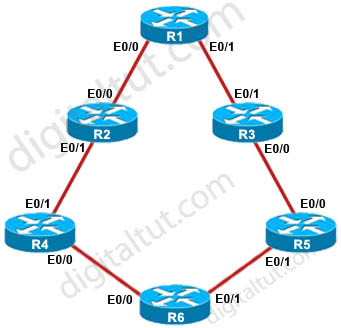
The configuration of R1 to R6 are posted below for your reference, useless lines are omitted:
| R1 interface Loopback0 ip address 150.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface Ethernet0/0 description Link to R2 ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0 ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 1 20 ! interface Ethernet0/1 description Link to R3 ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.0 ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 1 20 delay 5773 ! router eigrp 1 network 192.168.12.0 network 192.168.13.0 net 150.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 variance 11 |
R2 interface Ethernet0/0 description Link to R1 ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/1 description Link to R4 ip address 192.168.24.2 255.255.255.0 ip authentication mode eigrp 1 md5 ip authentication key-chain eigrp 1 CISCO ! router eigrp 1 network 192.168.12.0 network 192.168.24.0 ! key chain CISCO key 1 key-string firstkey key chain FIRSTKEY key 1 key-string CISCO key chain R3 key 1 key-string R3 key 2 key-string R1 |
R3 interface Ethernet0/0 description Link to R5 ip address 192.168.35.3 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/1 description Link to R1 ip address 192.168.13.3 255.255.255.0 ! router eigrp 1 network 192.168.13.0 network 192.168.35.0 |
| R4 interface Loopback0 ip address 150.1.4.4 255.255.255.255 ! interface Ethernet0/0 description Link to R6 ip address 192.168.46.4 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/1 description Link to R2 ip address 192.168.24.4 255.255.255.0 ip authentication mode eigrp 1 md5 ip authentication key-chain eigrp 1 CISCO ! router eigrp 1 network 192.168.46.0 network 192.168.24.0 network 150.1.4.4 0.0.0.0 ! key chain CISCO key 1 key-string firstkey |
R5 interface Ethernet0/0 description Link to R3 ip address 192.168.35.5 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/1 description Link to R6 ip address 192.168.56.5 255.255.255.0 ! router eigrp 1 network 192.168.35.0 network 192.168.56.0 |
R6 interface Loopback0 ip address 150.1.6.6 255.255.255.255 ! interface Loopback1 ip address 172.16.6.6 255.255.255.255 ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 192.168.46.6 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/1 ip address 192.168.56.6 255.255.255.0 ! router eigrp 1 distribute-list 1 out network 150.1.6.6 0.0.0.0 network 172.16.6.6 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.46.0 network 192.168.56.0 ! access-list 1 permit 192.168.46.0 access-list 1 permit 192.168.56.0 access-list 1 permit 150.1.6.6 access-list 1 deny 172.16.6.6 access-list 2 permit 192.168.47.1 access-list 2 permit 192.168.13.1 access-list 2 permit 192.168.12.1 access-list 2 deny 150.1.1.1 |
Note: This sim uses IOS version 15 so “no auto-summary” is the default setting of EIGRP. You don’t have to type it.
You can download this sim to practice at http://www.digitaltut.com/download/ROUTE_EIGRP.zip. Please use GNS3 with version older than v1.0 to open it (v0.8.3.1 for example). IOS used in this lab: c3640-jk9s-mz.124-16.bin
Question 1
Explanation
First we need to get the IP address of R6’s loopback address by “show ip interface brief” command on R6:
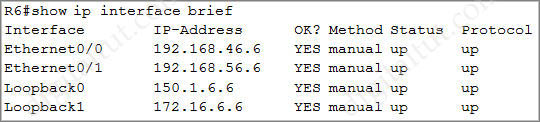
Now we learned the R6’s loopback address is 150.1.6.6. To see the ratio of traffic that is load shared between paths, use the “show ip route 150.1.6.6” command on R1:
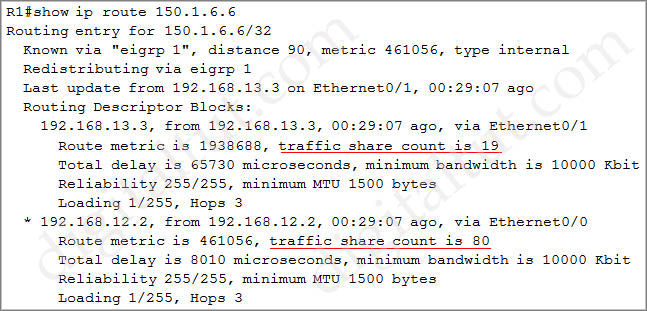
This means that after 19 packets are sent to 192.168.13.3, R1 will send 80 packets to 192.168.12.2 (ratio 19:80). This is unequal cost path Load balancing (configured with “variance” command).
Question 2
Explanation
Use the “show running-config” on R6 we will see a distribute-list applying under EIGRP:
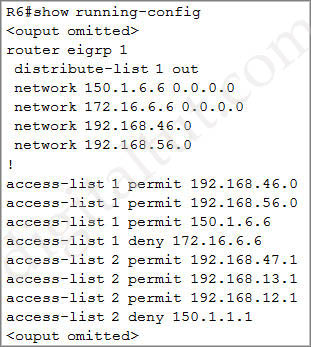
With this distribute-list, only networks 192.168.46.0; 192.168.56.0 and 150.1.6.6 are advertised out by R6.
Question 3
Explanation
Check on both R2 and R4:
 |
 |
To successfully authenticate between two EIGRP neighbors, the key number and key-string must match. The key chain name is only for local use. In this case we have key number “1” and key-string “CISCO” and they match so EIGRP neighbor relationship is formed.
Question 4
Explanation
To check the advertised distance for a prefix we cannot use the “show ip route” command because it only shows the metric (also known as Feasible Distance). Therefore we have to use the “show ip eigrp topology” command:

Update: Although the “show ip eigrp topology” does not work in the exam but the “show ip eigrp 1 topology” does work so please use this command instead and we will find out the advertised distance on R1.
There are two parameters in the brackets of 192.168.46.0/24 prefix: (1810944/333056). The first one “1810944” is the Feasible Distance (FD) and the second “333056” is the Advertised Distance (AD) of that route -> A is correct.
Just for your reference, this is the output of the “show ip route” command on R1:
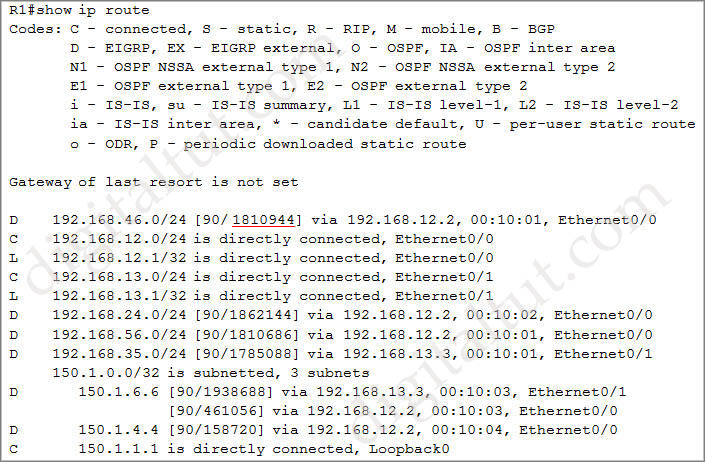
In the first line:
| D 192.168.46.0/24 [90/ 1810944] via 192.168.12.2, 00:10:01, Ethernet0/0 |
The first parameter “90” is the EIGRP Administrative Distance. The second parameter “1810944” is the metric of the route 192.168.46.0/24. R1 will use this metric to advertise this route to other routers but the question asks about “the advertised distance for the 192.168.46.0 network on R1” so we cannot use this command to find out the answer.
Question 5
Explanation
Check with the “show running-config” command on R1:
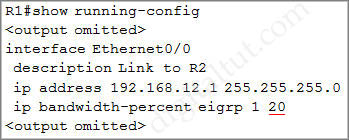
In the “ip bandwitdh-percent eigrp 1 20” command, “1” is the EIGRP AS number while “20” is the percent of interface’s bandwidth that EIGRP is allowed to use.
Note: By default, EIGRP uses up to 50% of the interface bandwidth. The bandwidth-percent value can be configured greater than 100%. It is useful when we set interface bandwidth lower than the real capacity of the link (for policy reasons, for example).


