Virtualization Questions 2
Question 1
Explanation
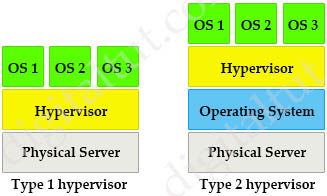
In contrast to type 1 hypervisor, a type 2 hypervisor (or hosted hypervisor) runs on top of an operating system and not the physical hardware directly. A big advantage of Type 2 hypervisors is that management console software is not required. Examples of type 2 hypervisor are VMware Workstation (which can run on Windows, Mac and Linux) or Microsoft Virtual PC (only runs on Windows).
Question 2
Explanation
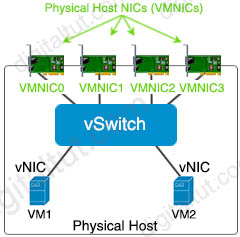
Hypervisors provide virtual switch (vSwitch) that Virtual Machines (VMs) use to communicate with other VMs on the same host. The vSwitch may also be connected to the host’s physical NIC to allow VMs to get layer 2 access to the outside world.
Each VM is provided with a virtual NIC (vNIC) that is connected to the virtual switch. Multiple vNICs can connect to a single vSwitch, allowing VMs on a physical host to communicate with one another at layer 2 without having to go out to a physical switch.
-> Therefore answer B is correct.
Answer E is not correct as besides the virtual switch running as a separate virtual machine, we also need to set up a trunk link so that VMs can communicate.
Answer C is not correct as it is too complex when we want to connect two VMs on the same hypervisor. VXLAN should only be used between two VMs on different physical servers.
Answer D is not correct as it uses Layer 3 network (routed link).
Therefore only answer A is left. We can connect two VMs via a trunk link with an external Layer2 switch.
Question 3
Explanation
There are two types of hypervisors: type 1 and type 2 hypervisor.
In type 1 hypervisor (or native hypervisor), the hypervisor is installed directly on the physical server. Then instances of an operating system (OS) are installed on the hypervisor. Type 1 hypervisor has direct access to the hardware resources. Therefore they are more efficient than hosted architectures. Some examples of type 1 hypervisor are VMware vSphere/ESXi, Oracle VM Server, KVM and Microsoft Hyper-V.
In contrast to type 1 hypervisor, a type 2 hypervisor (or hosted hypervisor) runs on top of an operating system and not the physical hardware directly. A big advantage of Type 2 hypervisors is that management console software is not required. Examples of type 2 hypervisor are VMware Workstation (which can run on Windows, Mac and Linux) or Microsoft Virtual PC (only runs on Windows).

Question 4
Explanation
Each VM is provided with a virtual NIC (vNIC) that is connected to the virtual switch. Multiple vNICs can connect to a single vSwitch, allowing VMs on a physical host to communicate with one another at layer 2 without having to go out to a physical switch.

Question 5
Explanation
There are two types of hypervisors: type 1 and type 2 hypervisor.
In type 1 hypervisor (or native hypervisor), the hypervisor is installed directly on the physical server. Then instances of an operating system (OS) are installed on the hypervisor. Type 1 hypervisor has direct access to the hardware resources. Therefore they are more efficient than hosted architectures. Some examples of type 1 hypervisor are VMware vSphere/ESXi, Oracle VM Server, KVM and Microsoft Hyper-V.
In contrast to type 1 hypervisor, a type 2 hypervisor (or hosted hypervisor) runs on top of an operating system and not the physical hardware directly. A big advantage of Type 2 hypervisors is that management console software is not required. Examples of type 2 hypervisor are VMware Workstation (which can run on Windows, Mac and Linux) or Microsoft Virtual PC (only runs on Windows).
Type 1 is more efficient and well performing, it is also more secure than type 2 because the flaws and vulnerabilities that are endemic to Operating Systems are often absent from Type 1, bare metal hypervisors. Type 1 has better performance, scalability and stability but supported by limited hardware.

Question 6
Explanation
Static routes directly between VRFs are not supported so we cannot configure a direct static route between two VRFs.
The command “ip route vrf Customer1 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.1.1 global” means in VRF Customer1, in order to reach destination 172.16.1.0/24 then we uses the next hop IP address 172.16.1.1 in the global routing table. And the command “ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 Vlan10” tells the router “to reach 192.168.1.0/24, send to Vlan 10”.
Question 7
Explanation
This question is a bit unclear but it mentioned about “dedicated operating systems that provide the virtualization platform” -> It means the Hypervisor so “Type 1 hypervisor” is the best choice here as type 1 hypervisor does not require to run any underlay Operating System.
Note: Hosted virtualization is type 2 hypervisor. In contrast to type 1 hypervisor, a type 2 hypervisor (or hosted hypervisor) runs on top of an operating system and not the physical hardware directly. A big advantage of Type 2 hypervisors is that management console software is not required. Examples of type 2 hypervisor are VMware Workstation (which can run on Windows, Mac and Linux) or Microsoft Virtual PC (only runs on Windows).




ADMIN… can you look into Q 2… many sites are reporting correct answer as B, D
^ Q2 has me confused as well
Q2: Correct answers are
A. Use a single trunk link to an external Layer2 switch
B. Use a virtual switch provided by the hypervisor.
On switchport itself configure as trunk port, connect to hypervisor NIC card.
From the vSwitch itself, specify VLANs to individual virtual machine.
contoso:
If the vlan is the same, then the external switch is not needed. Becouse vSwitch will not allow frames to be sent out. A Layer 2 switch will not solve the intervlan connection problem.
Q7 should be B??? Type 1 hypervisor
In the question they say dedicated OS that PROVIDES the virtualization platform. So the OS provide the VM functionality.
And the question is “What is this operating system described as?” What is the operating system? A operating system isn’t a “hosted virtualization”
If they would mean “hosted virtualization”, they would ask “What kind of virtualization is this?”
Please correct me if I’m wrong.
I agree with RM
@Digitaltut, can you please provide your feedback on queries raised on Question 2 and Question 7
The wording for question 7 seems very bad, so is probably wrong. “What is this operating system described as?” surely it should be something more like what is this architecture described as?
@cert, @Anonymous: For Q2, we believe A B are the correct answers and we provided the explanation.
Hi, Q2 in PDF has other answers (B and E) than on this page (A and B).
@digitaltut – Q2 – B,E are best answers.
Explanation:
B. Use a virtual switch provided by the hypervisor
E. Use a virtual switch running as a separate virtual machine
Both of above do not need any additional HW nor physical cabling and can run in hypervisor. In fact those are most common setups in real production.
Your explanation is not correct:
Answer E is not correct as besides the virtual switch running as a separate virtual machine, we also need to set up a trunk link so that VMs can communicate.
>> You don’t need “to set up a trunk link” you can attach VMs vNICs to the switch port running as a VM (i.e. Nexus 9000v Switch) directly in hypervisor
Why others are wrong or not best:
A. Use a single trunk link to an external Layer2 switch >> Not best – require additional HW & cabling
C. Use VXLAN fabric after installing VXLAN tunnelling drivers on the virtual machines >> Not best – require VXLAN fabric usually in form of additional HW and cabling
D. Use a single routed link to an external router on stick >> not correct as it still require L2 switch and provide L3 connectivity not L2 connectivity.
Dear Diditaltut,
Q6 in all answers is typo of 192.168.1.200, it should be 192.168.1.1
Kindly update
Q7 is absolute crap
Question 7
A customer has deployed an environment with shared storage to allow for the migration of virtual machines between servers with dedicated operating systems that provide the virtualization platform. What is this operating system described as?
A. hosted virtualization
B. type 1 hypervisor
C. container oriented
D. decoupled
The Answer should be A.
Question 7
“Question 7
“Virtual machines between servers with dedicated operating systems” , that with Type 2 Hypervisor, isn’t it?
https://www.freecram.net/question/Cisco.350-401.v2021-08-13.q147/a-customer-has-deployed-an-environment-with-shared-storage-to-allow-for-the-migration-of-virtual-machines