Operations Questions
Here you will find answers to Operation questions
Question 1
Which three route filtering statements are true? (Choose three)
A – After the router rip and passive-interface s0/0 commands have been issued, the s0/0 interface will not send any RIP updates, but will receive routing updates on that interface.
B – After the router eigrp 10 and passive-interface s0/0 commands have been issued, the s0/0 interface will not send any EIGRP updates, but will receive routing updates on that interface
C – After the router ospf 10 and passive-interface s0/0 commands have been issued , the s0/0 interface will not send any OSPF updates, but will receive routing updates on that interface
D – When you use the passive-interface command with RIPv2, multicasts are sent out the specified interface
E – When you use the passive-interface command with EIGRP, hello messages are not sent out the specified interface
F – When you use the passive-interface command with OSPF, hello messages are not sent out the specified interface
Answer: A E F
Explanation
Passive-interface command is used in all routing protocols to disable sending updates out from a specific interface. However the command behavior varies from one protocol to another”
– In RIP, this command will not allow sending multicast updates via a specific interface but will allow listening to incoming updates from other RIP speaking neighbors. This means that the router will still be able to receive updates on that passive interface and use them in its routing table.
In EIGRP and OSPF the passive-interface command stops sending outgoing hello packets, hence the router can not form any neighbor relationship via the passive interface. This behavior stops both outgoing and incoming routing updates.
Question 2
Which functionality is required within an IP router that is situated at the boundary of an IPv4 network and an IPv6 network to allow communication between IPv6-only and IPv4-only nodes?
A. Autoconfiguration
B. Automatic 6to4 Tunnel
C. Automatic 6to4 Relay
D. Network Address Translator-Protocol Translator (NAT-PT)
E. Intrasite Automatic Tunnel Address Protocol (ISATAP)
Answer: D
Explanation
The Network Address Translator – Protocol Translator (NAT-PT) defines a set of network-layer translation mechanisms designed to allow nodes that only support IPv4 to communicate with nodes that only support IPv6, during the transition to the use of IPv6 in the Internet.
NAT-PT provides IPv4/IPv6 protocol translation. It resides within an IP router, situated at the boundary of an IPv4 network and an IPv6 network. By installing NAT-PT between an IPv4 and IPv6 network, all IPv4 users are given access to the IPv6 network without modification in the local IPv4-hosts (and vice versa). Equally, all hosts on the IPv6 network are given access to the IPv4 hosts without modification to the local IPv6-hosts. This is accomplished with a pool of IPv4 addresses for assignment to IPv6 nodes on a dynamic basis as sessions are initiated across IPv4-IPv6 boundaries
(Reference: http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc4966.txt and http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/iosswrel/ps8802/ps6969/ps1835/prod_white_paper09186a008011ff51_ps6640_Products_White_Paper.html)
Question 3
Which DSL encapsulation method requires client software running on the end-user PC that is directly connected to a DSL modem?
A. PPPoA
B. PPPoE
C. PPP
D. L2TP
E. ATM
Answer: B
Question 4
What is the purpose of configuring the router as a PPPoE client?
A. to provide VPN access over L2TP
B. to enable PPP session from the router to the termination device at the headend for metro Ethernet connectivity
C. for DSL connectivity and removing the need for the end-user PC to run the PPPoE client software
D. for connecting the router to a cable modem, which bridges the Ethernet frames from the router to the cable modem termination system
Answer: C
Question 5
What is the international standard for transmitting data over a cable system?
A. PPPoE
B. DOCSIS
C. CMTS
D. AAL5
Answer: B
Explanation
Data Over Cable Service Interface Specifications (DOCSIS) is a method for transporting data over a cable (CATV) plant utilizing QAM and/or QPSK RF modulatio. DOCSIS specifies modulation schemes and the protocol for exchanging bidirectional signals over cable. The DOCSIS has been approved as an international standard for transmitting data over cable systems.
Question 6
Under which circumstance will a branch ISR router contain interface vlan configurations?
A. performing inter-VLAN routing
B. performing 802.1Q trunking
C. performing ISL trunking
D. Ethernet Switch Module installed
E. ADSL WIC installed
F. running Call Manager Express
Answer: D
Explanation
An Integrated Services Router(ISR) router can be implemented an Ethernet Switch Module to perform both IP routing and inter-VLAN routing. With this module, an ISR router will contain interface vlan configurations.
Question 7
Which of the following are true? (choose three)
A. For Frame Relay point-to-point interfaces, set the bandwidth to the CIR.
B. For Frame Relay point-to-point interfaces set the bandwidth to the sum of all CIRs.
C. For Frame Relay multipoint connections, set the bandwidth to the sum of all CIRs.
D. For generic serial interfaces such as PPP and HDLC, set the bandwidth to match the line speed.
E. For Frame Relay multipoint connections, set the bandwidth to the CIR.
Answer: A C D
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit. What is the correct configuration to enable router R4 to exchange RIP routing updates with router R1 but not with router R3?
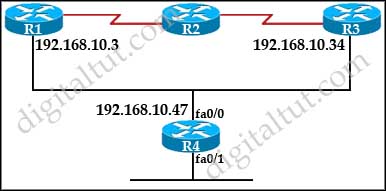
A.
R4(config)# interface fa0/0
R4(config-if)# neighbor 192.168.10.3
R4(config-if)# passive-interface fa0/0
B.
R4(config)# router rip
R4(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.10.3
R4(config-router)#passive-interface fa0/0
C.
R4(config)# interface fa0/0
R4(config-if)# neighbor 192.168.10.3
R4(config-if)# passive-interface 192.168.10.34
D.
R4(config)# router rip
R4(config-router)# neighbor 162.168.10.34 no broadcast
R4(config-router)#passive-interface fa0/0
Answer: B
Explanation
The “neighbor 192.168.10.3” command in RIP will make that router to send unicast update to 192.168.10.3 while the “passive-interface …” command is used to disable sending multicast or broadcast updates out of a specific interface. The key point here is the “passive-interface” still allows to send unicast update so it can be used along with the “neighbor …” command.
Question 9
Refer to exhibit. RA (DR) failed, and after 10 minutes it came back. Which two statements are true? (Choose two)
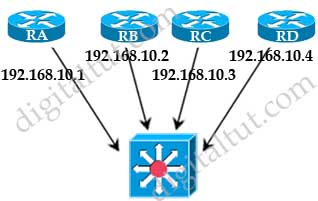
A. RA is a DR
B. RA is a BDR
C. RA is a DROTHER
D. RB is a DR
E. RB is a BDR
F. RC is a DROTHER
Answer: C D(?)
Explanation
This question is missing some information. We don’t know before RA failed, who the BDR was. Suppose RB was the BDR before RA failed then RB would be the DR even when RA comes back. When RA comes back, its segment has both DR and BDR elected so RA will take the DROTHER role -> C is correct but D is missing information.
Question 10
A router has been configured to filter routes. Which of the following are reasons to control routing updates via route filtering? (Choose three)
A. to hide certain networks from the rest of organization
B. for easier implementations
C. to control network overhead on the wire
D. for simple security
E. to prevent adjacencies from forming
Answer: A C D


