CEF & Fast Switching
|
CEF Quick summary: Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) provides the ability to switch packets through a device in a very quick and efficient way while also keeping the load on the router’s processor low. CEF is made up of two different main components: the Forwarding Information Base (FIB) and the Adjacency Table. These are automatically updated at the same time as the routing table. The adjacency table is tasked with maintaining the layer 2 next-hop information for the FIB. Adjacency Types That Require Special Handling: Glean adjacency – in short when the router is directly connected to hosts the FIB table on the router will maintain a prefix for the subnet rather than for the individual host prefix. This subnet prefix points to a GLEAN adjacency. A glean adjacency entry indicates that a particular next hop should be directly connected, but there is no MAC header rewrite information available. When the device needs to forward packets to a specific host on a subnet, Cisco Express Forwarding requests an ARP entry for the specific prefix, ARP sends the MAC address, and the adjacency entry for the host is built. Other special adjacency types are Discard adjacency and Drop adjacency but they are not mentioned here. |
Question 1
Explanation
The command “show ip cef” is used to display the CEF Forwarding Information Base (FIB) table. There are some entries we want to explain:
+ If the “Next Hop” field of a network prefix is set to receive, the entry represents an IP address on one of the router’s interfaces. In this case, 192.168.201.2 and 192.168.201.31 are IP addresses assigned to interfaces on the local router.
+ If the “Next Hop” field of a network prefix is set to attached, the entry represents a network to which the router is directly attached. In this case the prefix 192.168.201.0/27 is a network directly attached to router R2’s Fa0/0 interface.
But there are some special cases:
+ The all-0s host addresses (for example, 192.168.201.0/32) and the all-1s host addresses (not have in the output above but for example, 192.168.201.255/32) also show as receive entries.
+ 255.255.255.255/32 is the local broadcast address for a subnet
+ 0.0.0.0/32: maybe it is a reserved link-local address
+ 0.0.0.0/0: This is the default route that matching all other addresses (also known as “gateway of last resort”). In this case it points to 192.168.201.1 -> Answer C is correct.
Reference: CCNP Routing and Switching ROUTE 300-101 Official Cert Guide
Question 2
Explanation
The “show adjacency” command is used to display information about the Cisco Express Forwarding adjacency table or the hardware Layer 3-switching adjacency table.
There are two known reasons for an incomplete adjacency:
+ The router cannot use ARP successfully for the next-hop interface.
+ After a clear ip arp or a clear adjacency command, the router marks the adjacency as incomplete. Then it fails to clear the entry.
Note: Two nodes in the network are considered adjacent if they can reach each other using only one hop.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/express-forwarding-cef/17812-cef-incomp.html
Question 3
Explanation
The “show ip cache” command displays the contents of a router’s fast cache. An example of the output of this command is shown below:
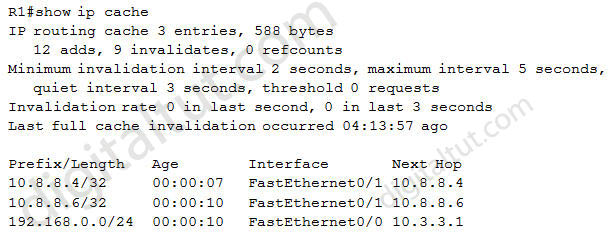
Note: If CEF is disabled and fast switching is enabled, the router begins to populate its fast cache.
Question 4
Question 5
Explanation
Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) provides the ability to switch packets through a device in a very quick and efficient way while also keeping the load on the router’s processor low. CEF is made up of two different main components: the Forwarding Information Base (FIB) and the Adjacency Table. These are automatically updated at the same time as the routing table.
The adjacency table is tasked with maintaining the layer 2 next-hop information for the FIB.
Question 6
Explanation
The explanation of this question is too lengthy so we recommend to read this article: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/express-forwarding-cef/26083-trouble-cef.html
Question 7
Explanation
Glean adjacency – in short when the router is directly connected to hosts the FIB table on the router will maintain a prefix for the subnet rather than for the individual host prefix. This subnet prefix points to a GLEAN adjacency.
Punt adjacency – When packets to a destination prefix can’t be CEF Switched, or the feature is not supported in the CEF Switching path, the router will then use the next slower switching mechanism configured on the router.
Question 8
Explanation
Nodes in the network are said to be adjacent if they can reach each other with a single hop across a link layer. In addition to the FIB, CEF uses adjacency tables to prepend Layer 2 addressing information. The adjacency table maintains Layer 2 next-hop addresses for all FIB entries.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios/12_2/switch/configuration/guide/fswtch_c/xcfcef.html
Question 9



About Q4 I think there is an incorrect question. No answers are valid there. The correct answer should be “punt”, i.e. “sending a packet to the next fastest switching level”. I think so.
On Q4 – Punt is still an entry, so if there isn’t an entry, it is dropped.
https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/thread/86875
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/express-forwarding-cef/17812-cef-incomp.html
I agree with Marcus about Q4. Should be next slower engine, that is punt. No reason to drop first packet when ARP entry is not defined yet or fir similar reasons.
But I am confused by Q2. Serial lines don’t use ARP. FR Inverse ARP and HDLC SLARP are different technologies. Reference provided address ethernet type interface behavior.
Latest update 100% valid CCNP Exam questions
dumps
pro
dot
com
Q2.
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/express-forwarding-cef/17812-cef-incomp.html
Q4- The FIB table is the replication of the routing table but hardware based. thus if the entry is not in the routing table, the packet will be dropped. So B is correct!
Share a useful link, the content inside is true and effective.
I purchased 300-101, the information inside is true and effective. Before the exam, the question bank will be updated to take the initiative to communicate with me. The attitude is very good. Any questions will be answered in time, and the information is comprehensive. There is no subject. I passed the exam and shared it with you. I hope it will help you too.
h tt p://t .cn/RDug3fQ
W ww.cci
edumps.xyz?utm_source=bbs&utm_medium=bbs
I just passed the CCIE exam last week. I bought the topic here. The topic is true and effective. I have practiced most of the exam questions, but you have to remember the answer. You can’t just remember it. The options, I have encountered several questions in it, the options for the correct answer have been changed.
I agree with Hasho. Is the confusion related to terms. Q4 is very clear “without an FIB entry”
Punt is an ENTRY in CEF Table. Look for example in Q7. Reason for be punt adjacency is interface type (tunnel). For that type of traffic, switching is done by slowest method (fast switching, or worst, process switching).
So, when no FIB entry is exactly the same with no route info for that destination packet. What is happened when no route is for packet?. Is dropped. Only difference in our case, is the fact everything is happened in CEF.
Please email the latest dump for 300-101 = jun_ieccomputers at yahoo dot com
Contact below email for sharing updated dump: network4career@ gmail . com
Can anyone explain Q9? Couldn’t find resource on in.
hi all good day, I’m chasing the CCNP route exam. I hope to get it before the migration. Please share with me the latest dumps for this exam in the email below. I really appreciate if you will include the VCE file for this thank you.
remove: S P A C E and replace 0 (zero) to o (ohw)
cj clds_cj @ yah00.c0m
HI all please can anyone send me dump viled i hop so thanks dears
gadorashaker (@)(gmail)(.com)
Hi ALL,
Just passed CCNA. Want to start preparing for CCNP.
Anyone with pdf material or book for 350-401 and 350-410 please share email address. I will contact you.
Thank you.
Hi there,
I don’t see questions just answers??