IPSec and GRE
Here you will find answers to IPSec and GRE questions
Question 1
What two features are benefits of using GRE tunnels with IPsec over using IPsec tunnel alone for building site-to-site VPNs? (Choose two)
A. allows dynamic routing securely over the tunnel
B. IKE keepalives are unidirectional and sent every ten seconds
C. reduces IPsec headers overhead since tunnel mode is used
D. supports non-IP traffic over the tunnel
E. uses Virtual Tunnel Interface (VTI)to simplify the IPsec VPN configuration
Answer: A D
Explanation
A drawback of IPSec is it does not support multicast traffic. But most popular routing protocols nowadays rely on multicast (like OSPF, EIGRP, RIP… except BGP) to send their routing updates. A popular solution to this is using GRE tunnels. GRE tunnels do support transporting IP multicast and broadcast packets to the other end of the GRE tunnel -> A is correct.
Non-IP traffic (such as IPX, AppleTalk) can be wrapped inside GRE encapsulation and then this packet is subjected to IPSec encapsulation so all traffic can be routed -> D is correct.
Question 2
Which statement is true about an IPsec/GRE tunnel?
A. The GRE tunnel source and destination addresses are specified within the IPsec transform set.
B. An IPsec/GRE tunnel must use IPsec tunnel mode.
C. GRE encapsulation occurs before the IPsec encryption process.
D. Crypto map ACL is not needed to match which traffic will be protected.
Answer: C
Explanation
When running GRE tunnel over IPSec, a packet is first encapsulated in a GRE packet and then GRE is encrypted by IPSec -> C is correct.
Question 3
Which of the following is a GRE Tunnel characteristic?
A. GRE impose more CPU overhead than IPSec on VPN gateways
B. GRE tunnels can run through IPsec tunnels.
C. GRE Tunnel doesn’t have support for IPv6
D. GRE consists of two sub-protocols: Encapsulated Security Payload (ESP) and Authentication Header (AH).
Answer: B
Question 4
What is a key benefit of using a GRE tunnel to provide connectivity between branch offices and headquarters?
A. authentication, integrity checking, and confidentiality
B. less overhead
C. dynamic routing over the tunnel
D. granular QoS support
E. open standard
F. scalability
Answer: C
Explanation
GRE tunnel provides a way to encapsulate any network layer protocol over any other network layer protocol. GRE allows routers to act as if they have a virtual point-to-point connection to each other. GRE tunneling is accomplished by creating routable tunnel endpoints that operate on top of existing physical and/or other logical endpoints. Especially, IPsec does not support multicast traffic so GRE tunnel is a good solution instead (or we can combine both).
Question 5
What are the four main steps in configuring a GRE tunnel over IPsec on Cisco routers? (Choose four)
A. Configure a physical interface or create a loopback interface to use as the tunnel endpoint.
B. Create the GRE tunnel interfaces.
C. Add the tunnel interfaces to the routing process so that it exchanges routing updates across that interface.
D. Add the tunnel subnet to the routing process so that it exchanges routing updates across that interface.
E. Add all subnets to the crypto access-list, so that IPsec encrypts the GRE tunnel traffic.
F. Add GRE traffic to the crypto access-list, so that IPsec encrypts the GRE tunnel traffic.
Answer: A B D F
Explanation
Four steps to configure GRE tunnel over IPsec are:
1. Create a physical or loopback interface to use as the tunnel endpoint. Using a loopback rather than a physical interface adds stability to the configuration.
2. Create the GRE tunnel interfaces.
3. Add the tunnel subnet to the routing process so that it exchanges routing updates across that interface.
4. Add GRE traffic to the crypto access list, so that IPsec encrypts the GRE tunnel traffic.
An example of configuring GRE Tunnel is shown below:
interface Tunnel0
ip address 192.168.16.2 255.255.255.0
tunnel source FastEthernet1/0
tunnel destination 14.38.88.10
tunnel mode gre ip
Note: The last command is enabled by default so we can ignore it in the configuration)
(Reference: CCNP Routing and Switching Quick Reference)
Question 6
A network administrator uses GRE over IPSec to connect two branches together via VPN tunnel. Which one of the following is the reason for using GRE over IPSec?
A. GRE over IPSec provides better QoS mechanism and is faster than other WAN technologies.
B. GRE over IPSec decreases the overhead of the header.
C. GRE supports use of routing protocol, while IPSec supports encryption.
D. GRE supports encryption, while IPSec supports use of routing protocol.
Answer: C
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. A new TAC engineer came to you for advice. A GRE over IPsec tunnel was configured, but the tunnel is not coming up.
What did the TAC engineer configure incorrectly?
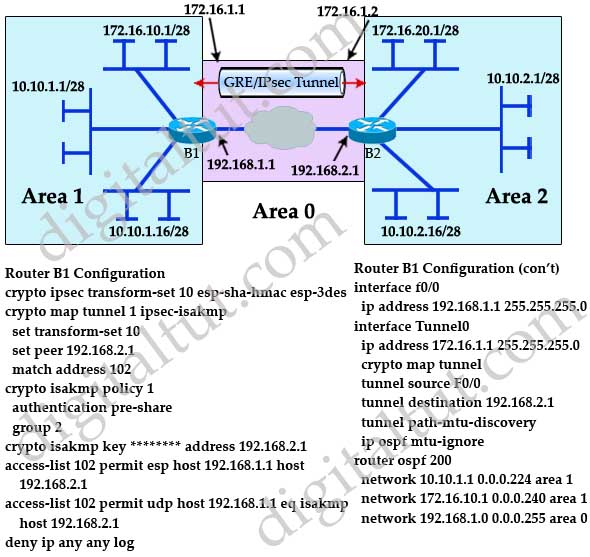
A. The crypto map is not configured correctly.
B. The crypto ACL is not configured correctly.
C. The crypto map is not applied to the correct interface.
D. The OSPF network is not configured correctly.
Answer: B
Explanation
The access-list must also support GRE traffic with the “access-list 102 permit gre host 192.168.1.1 host 192.168.2.1” command -> B is correct.
Below is the correct configuration for GRE over IPsec on router B1 along with descriptions.
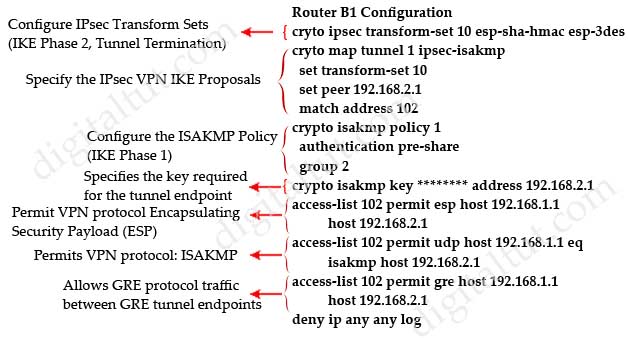
The interface tunnel configuration is rather simple so I don’t post it here.
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit. A new TAC engineer came to you for advice. A GRE over IPsec tunnel was configured, but the tunnel is not coming up.
What did the TAC engineer configure incorrectly?
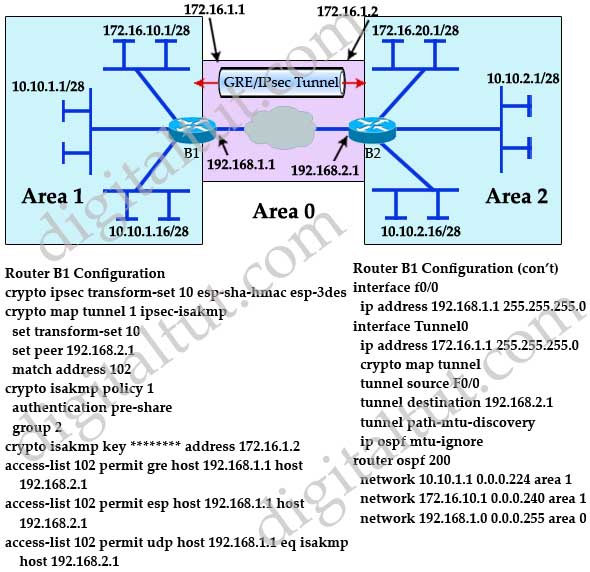
A. The crypto isakmp configuration is not correct.
B. The crypto map configuration is not correct.
C. The interface tunnel configuration is not correct.
D. The network configuration is not correct; network 172.16.1.0 is missing
Answer: A
Explanation
The address of the crypto isakmp key should be 192.168.1.2, not 172.16.1.2 -> A is correct.
Question 9
Refer to the exhibit. A new TAC engineer came to you for advice. A GRE over IPsec tunnel was configured, but the tunnel is not coming up.
What did the TAC engineer configure incorrectly?
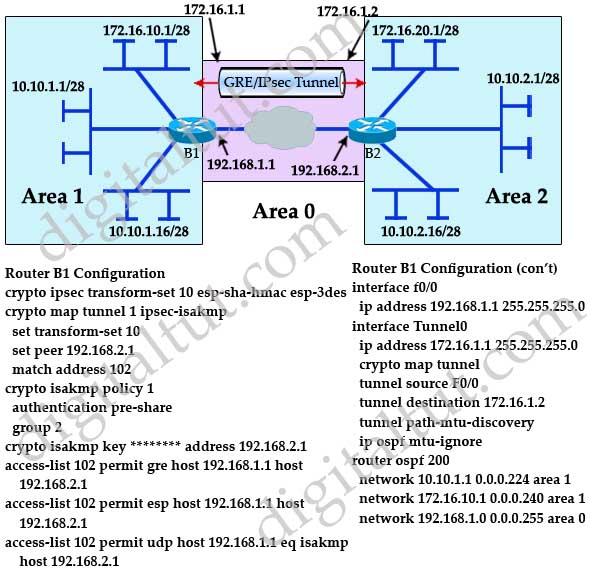
A. The crypto isakmp configuration is not correct.
B. The crypto map configuration is not correct.
C. The network 172.16.1.0 is not included in the OSPF process.
D. The interface tunnel configuration is not correct.
Answer: D
Explanation
The “tunnel destination” in interface tunnel should be 192.168.1.2, not 172.16.1.2 -> D is correct.
Question 10
For a GRE tunnel to be up between two routers, which of the following must be configured?
A. Loopback interface
B. IP reachability between the loopback interfaces
C. Dynamic Routing between routers.
D. Tunnel interfaces must be in the same subnet.
Answer: D
Question 11
Which two methods use IPsec to provide secure connectivity from the branch office to the headquarters office? (Choose two)
A. DMVPN
B. MPLS VPN
C. Virtual Tunnel Interface (VTI)
D. SSL VPN
E. PPPoE
Answer: A C
Explanation
The Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) feature allows users to better scale large and small IPSec VPNs by combining generic routing encapsulation (GRE) tunnels, IPSec encryption, and Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) to provide users with easy configuration through crypto profiles, which override the requirement for defining static crypto maps, and dynamic discovery of tunnel endpoints.
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk583/tk372/technologies_configuration_example09186a008014bcd7.shtml)
The use of VTI greatly simplifies the configuration process when you need to configure IPsec. A major benefit associated with IPsec VTIs is that the configuration does not require a static mapping of IPsec sessions to a physical interface.


