OSPF Questions 8
Here you will find answers to OSPF Questions – Part 8
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the information presented, which statement is true?
| RTA#show ip route ospf
O IA 6.0.0.0/8 [110/65] via 5.0.0.2, 00:00:18, Serial2/1/0 |
A. A default route is configured on the local router.
B. Network 6.0.0.0/8 was learned from an OSPF neighbor within the area.
C. OSPF router 5.0.0.2 is an ABR.
D. The default route is learned from an OSPF neighbor.
Answer: C
Explanation
The “O IA” here means”OSPF Inter-Area”. This means that RTA learned the route 6.0.0.0/8 from another OSPF neighbor outside its area. Moreover the “O*N2” is the LSA Type 7 which only appears on the ABR. You can read a lab about OSPF LSA Types here: http://www.digitaltut.com/ospf-lsa-types-lab.
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit. Given the exhibited router output, which command sequence can be added to R1 to generate a default route into the OSPF domain?
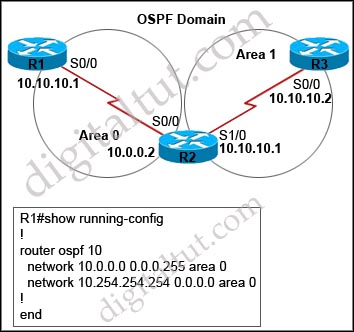
A. default-router
B. ip default-network
C. default-information originate always
D. ip default-gateway
Answer: C
Explanation
The default-information originate command advertises a default route to other routers, telling something like “please send me your unknown traffic”. With the always parameter, the default route is advertised even if there is no default route in the router’s routing table. In this case we don’t see any default route in the configuration of R1 (like ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 ….) so it must include the keyword “always” so that the default route is advertised.
Question 3
What are three kinds of OSPF areas? (Choose three)
A. stub
B. active
C. remote
D. backbone
E. ordinary or standard
Answer: A D E
Explanation
There are 4 kinds of OSPF areas:
+ Standard (Ordinary) Areas
+ Stub Areas
+ Totally Stubby Areas
+ Not-so-stubby Areas
Note: The backbone area (area 0) is also listed as a standard area.
Question 4
When implementing OSPFv3, which statement describes the configuration of OSPF areas?
A. In interface configuration mode, the OSPFv3 area ID combination assigns interfaces to OSPFv3 areas.
B. In router configuration mode, the network wildcard area ID combination assigns networks to OSPFv3 areas.
C. In interface configuration mode, the IPv6 OSPF process area ID combination assigns interfaces to OSPFv3 areas.
D. In router configuration mode, the IPv6 OSPF interface area ID combination assigns interfaces to OSPFv3 areas.
Answer: C
Explanation
An example of configuring IPv6 OSPF process area combined with OSPFv3 areas is shown below:
interface s1/0
ipv6 address 3FFE:B00:FFFF:1::2/64
ipv6 ospf 100 area 1
Note: OSPFv3 requires areas & OSPF process to be configured under interface, not in router mode.
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit. Why is the 140.140.0.0 network not used as the gateway of last resort even though it is configured first?
R3#show run | include default-
ip default-network 140.140.0.0
ip default-network 130.130.0.0
| R3#show ip route | begin Gateway Gateway of last resort is 0.0.0.0 to network 130.130.0.0 116.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 3 masks C 116.16.37.0/30 is directly connected, Serial1/0.2 C 116.16.32.0/30 is directly connected, Serial2/0.2 C 116.16.34.0/28 is directly connected, Serial1/0.1 C 116.16.35.0/28 is directly connected, Serial2/0.1 S 116.0.0.0/8 [1/0] via 116.16.34.0 * 140.140.0.0/32 is subnetted, 3 subnets O 140.140.1.1 [110/65J via 116.16.34.4, 00:14:54, Serial1/0.1 O 140.140.3.1 [110/65] via 116.16.34.4, 00:14:54, Serial1/0.1 O 140.140.2.1 [110/65] via 116.16.34.4, 00:14:54, Serial1/0.1 * 130.130.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks D* 130.130.0.0/16 is a summary, 00:30:04, Null0 C 130.130.1.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0 C 130.130.2.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/1 C 130.130.3.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet1/0 D 150.150.0.0/16 [90/679936] via 116.16.35.5, 00:02:58, Serial2/0.1 |
A. The last default-network statement will always be preferred.
B. A route to the 140.140.0.0 network does not exist in the routing table.
C. Default-network selection will always prefer the statement with the lowest IP address.
D. A router will load balance across multiple default-networks; repeatedly issuing the show ip route command would show the gateway of last resort changing between the two networks.
Answer: B
Explanation
In the routing table of R3, we can only see the route 130.130.0.0/16 is learned via EIGRP (marked with D) and is being chosen as the “Gateway of last resort”. The route to 140.140.0.0 is not present in the routing table so the command “ip default-network 140.140.0.0” has no effect. Remember that a route must appear in the routing table (via static route or learned via a routing protocol before it can be set as “Gateway of last resort” by the “ip default-network” command.
Question 6
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator wants to reduce the number of OSPF routes advertised from Area 1 into Area 2. As the router configuration specialist, what two things would you do to accomplish this goal? (Choose two)
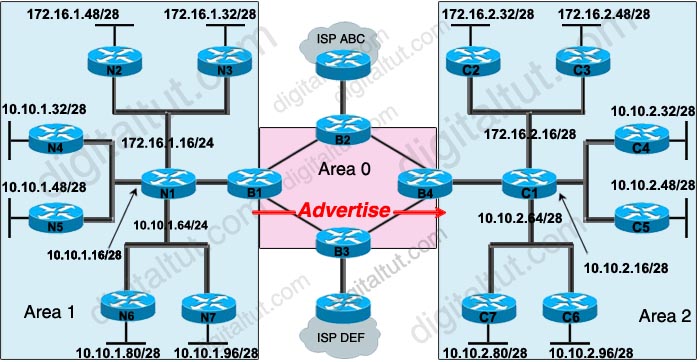
A. Enter the configuration on router B1.
B. Enter the configuration on router B4.
C. On the same router, enter the Summary-address 10.10.1.0 255.255.255.128 subcommand.
D. On the same router, enter the Area 1 range 10.10.1.0 255.255.255.128 subcommand.
E. On the same router, enter the Area 2 range 10.10.1.0 255.255.255.128 subcommand.
Answer: A D
Explanation
This is how to configure manual summarization on B1:
| router ospf 1 area 1 range 10.10.1.0 255.255.255.128 |
Question 7
Which command displays the number of times that the OSPF Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithm has been executed?
A. show ip protocol
B. show ip ospf interface
C. show ip ospf
D. show ip ospf database
Answer: C
Explanation
The output of the “show ip ospf” command is shown below:
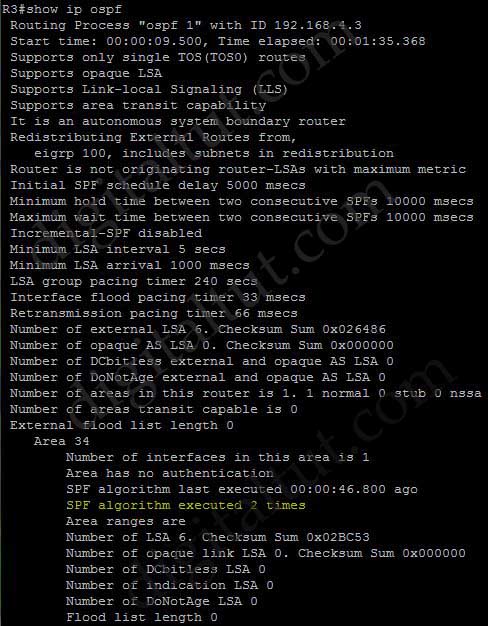
Question 8
For IPv6, what term or phrase best describes a type 9 LSA in OSPF?
A. router LSA
B. interarea prefix LSA
C. link LSA
D. interarea prefix LSA for ABRs
Answer: B
Question 9
Given the above OSPF network, which command will RTB use to summarize routes for the 192.168.16.0/22 supernet before injecting them into Area 0?
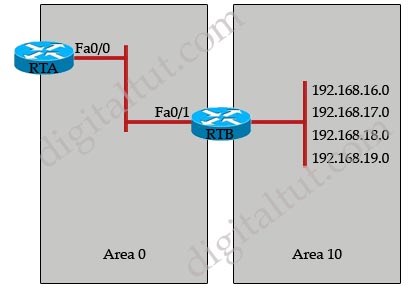
A. area 10 range 192.168.16.0 255.255.252.0
B. summary-address 192.168.16.0 255.255.252.0
C. ip summary-address ospf 101 192.168.16.0 255.255.252.0
D. area 0 range 192.168.16.0 255.255.252.0
E. ip summary-address area 0 192.168.16.0 255.255.252.0
Answer: A
Question 10
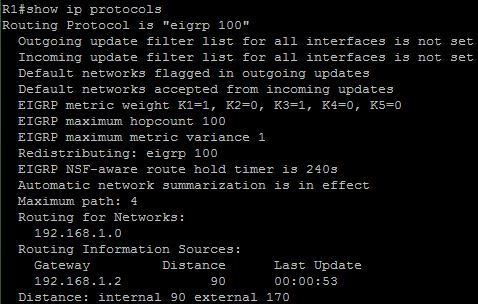
Which command would display OSPF parameters such as filters, default metric, maximum paths, and number of areas configured on a router?
A. show ip protocol
B. show ip route
C. show ip ospf interface
D. show ip ospf
Answer: A
Explanation
The output of the show ip protocol is shown below:
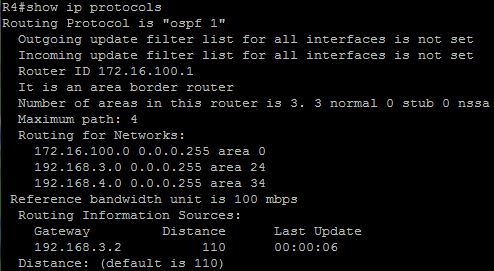
This command is used to display the parameters and current state of the active routing protocol process. This command displays all the filters (outgoing/incoming update filter list for all interfaces…), distance (default is 110 in this case for OSPF), metric (can be calculate by the formula 108 / Bandwidth), maximum paths (4, in this case), number of areas (3).
Below is the output of the same command but EIGRP is running, just for your reference: